Predicting wildlife reservoirs and global vulnerability to zoonotic Flaviviruses
Pranav S. Pandit, Megan M. Doyle, Katrina M. Smart, Cristin C.W. Young, Gaylen W. Drape & Christine K. Johnson
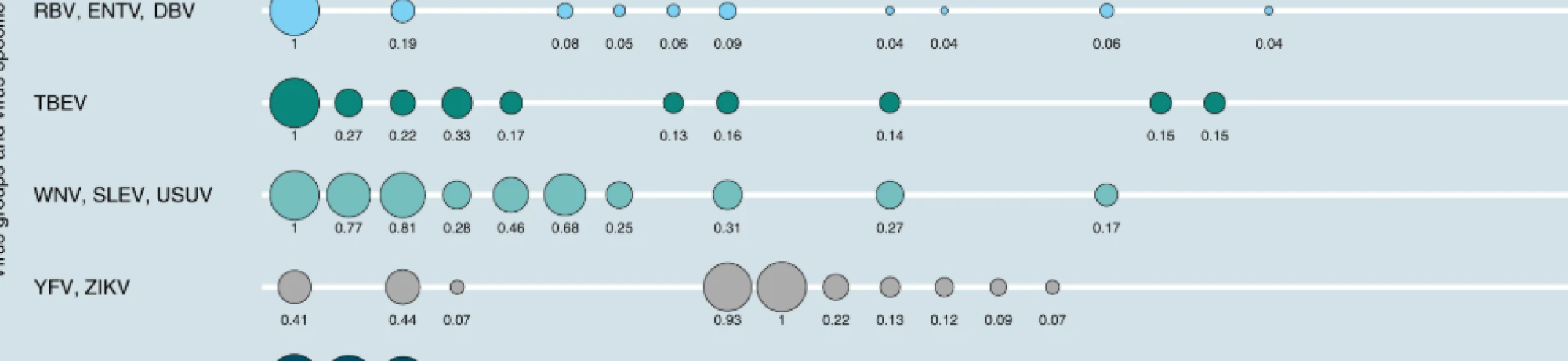
Flaviviruses pose significant public health risks and include pathogens such as Zika virus, West Nile virus, and Yellow Fever virus, which are transmitted through a wide diversity of mammalian and bird hosts.
Key Findings
- By employing a machine-learning modeling-based approach, our researchers were able to predict the probability of a species acting as a novel flavivirus host
- The model successfully identified ecological features of hosts and potential hosts that make them more likely to harbor these viruses, such as conservation status, geographical distribution, bioclimatic feature, and physiology
Informing Action
Results highlight host species and regions that should be monitored for flavivirus emergence vulnerability to mitigate the potential for viral spillover.